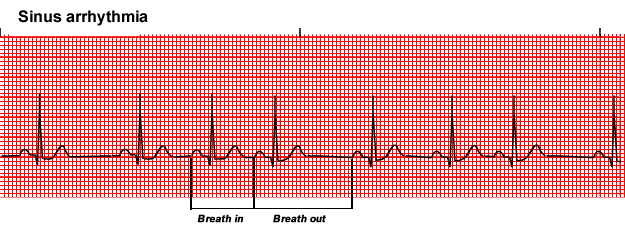
Sinus Arrhythmia

| Rate |
|
| P wave |
|
| QRS |
|
| Conduction |
|
| Rhythm |
|
The rate usually increases with inspiration and decreases with expiration.
This rhythm is most commonly seen with breathing due to fluctuations in parasympathetic vagal tone. During inspiration stretch receptors in the lungs stimulate the cardioinhibitory centers in the medulla via fibers in the vagus nerve.
The non respiratory form is present in diseased hearts and sometimes confused with sinus arrest (also known as "sinus pause").
Treatment is not usually required unless symptomatic bradycardia is present.
©RnCeus.com