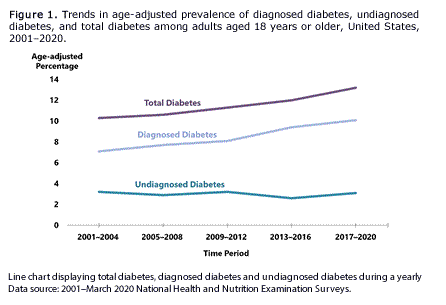
 During 2001–2020, the age-adjusted prevalence of total diabetes significantly increased among adults aged 18 years or older (Figure 1).
During 2001–2020, the age-adjusted prevalence of total diabetes significantly increased among adults aged 18 years or older (Figure 1). Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a complex group of disorders that result in hyperglycemia. Insufficient insulin production and/or resistance to the effects of insulin cause the hyperglycemia. Without the effect of insulin, the cells of the liver and skeletal muscle are unable to efficiently remove and store excess blood glucose.
Fast Facts on Diabetes
Trends in Prevalence of Diagnosed Diabetes, Undiagnosed Diabetes, and Total Diabetes
 During 2001–2020, the age-adjusted prevalence of total diabetes significantly increased among adults aged 18 years or older (Figure 1).
During 2001–2020, the age-adjusted prevalence of total diabetes significantly increased among adults aged 18 years or older (Figure 1).
More people are developing type 1 and type 2 diabetes during youth, and racial and ethnic minorities continue to develop type 2 diabetes at higher rates. Likewise, the proportion of older people in our nation is increasing, and older people are more likely to have a chronic disease like diabetes. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf
Chronic hyperglycemia of DM is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, blindness, kidney failure, and lower-limb amputation. The prevalence of DM is increasing in the United States.
Types of Diabetes
Reference
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). National Diabetes Statistics Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
©RnCeus.com