Opioid Tolerance, Dependency, and Addiction
- Chronic opioid use causes alterations in receptor sensitivity, leading to medication tolerance and changes in pain perception. Physiologic effects of opioids in the central nervous system are the result of activation of three main types of opioid receptors:
- Delta: analgesia, antidepressant, convulsant, physical dependence, modulate mu-related respiratory depression. (Theriot, Sabir & Azadfard, 2023).
- Kappa: analgesia, anticonvulsant, depression, hallucination, diuresis, dysphoria, miosis, neuroprotection, sedation. (Theriot Sabir,& Azadfard, 2023).
- Mu: analgesia, physical dependence, respiratory depression, miosis, euphoria, reduced GI motility, vasodilation.
- Peripheral mu receptors are tissue-specific with higher concentrations in bronchial smooth muscle and the digestive tract. This is the reason for opioids suppressing the cough reflex and causing constipation (Theriot Sabir, & Azadfard, 2023).
- Opioid tolerance occurs when a person using opioids begins to experience a reduced response to medication, requiring more opioids to experience the same effect
- Opioid dependence occurs when the body adjusts its normal functioning around regular opioid use. Unpleasant physical symptoms occur when medication is stopped.
- Opioid Use Disorder (OUD)) occurs when attempts to cut down or control use are unsuccessful or when use results in social problems and a failure to fulfill obligations at work, school, and home.
- Opioid addiction Opioid addiction often comes after the person has developed opioid tolerance and dependence, making it physically challenging to stop opioid use and increasing the risk of withdrawal (CDC, Opioids, rev. 2021).
- CDC - Opioid glossary
Tolerance to an opioid analgesic will require a larger dose of the drug to achieve the original pain-relieving effect. Physical dependence occurs when a patient who has been taking opioids on a long-term basis experiences withdrawal symptoms when the drug is abruptly stopped or when the patient is given an opioid antagonist. Patients should not be diagnosed as addicted based only on opioid dependence. Dependence is a universal physiological and pharmacological phenomenon that occurs following the regular use of opioids for more than two weeks. Opioid dependence is no different than dependence that occurs after administering steroids, beta blockers, and other antihypertensives for an extended period. As a result, opioid dependence is not evidence of opioid addiction.
Tolerance and physical dependence do occur in many patients after one to four weeks of regular use of opioid drugs. Under appropriate medical supervision, opioid use alone is the not the major factor in the development of addiction. Other biochemical, social, and psychological factors appear to play an important role in the development of addiction; addiction is a disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors that influence its development and manifestations.
Opioid Use Disorder and Opioid addiction
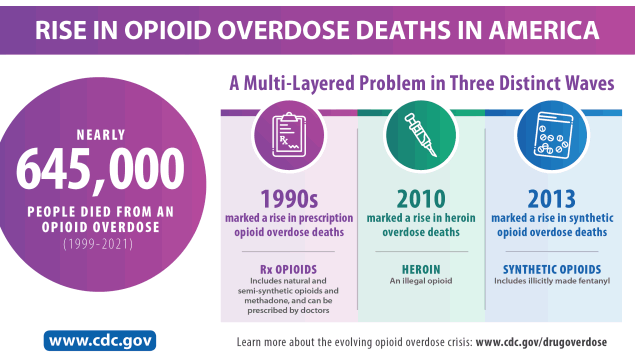 Opioid use disorder and opioid addiction remain at epidemic levels in the U.S. and worldwide. Three million US citizens and 16 million individuals worldwide have had or currently suffer from opioid use disorder (OUD).(Azadfard et al., 2023). The increase in OUD can be partially attributed to overprescribing of opioid medications. Healthcare providers in the 1990s increased opioid prescribing in response to the "pain as fifth vital sign" campaign.
Opioid use disorder and opioid addiction remain at epidemic levels in the U.S. and worldwide. Three million US citizens and 16 million individuals worldwide have had or currently suffer from opioid use disorder (OUD).(Azadfard et al., 2023). The increase in OUD can be partially attributed to overprescribing of opioid medications. Healthcare providers in the 1990s increased opioid prescribing in response to the "pain as fifth vital sign" campaign.
The CDC (2022) key facts
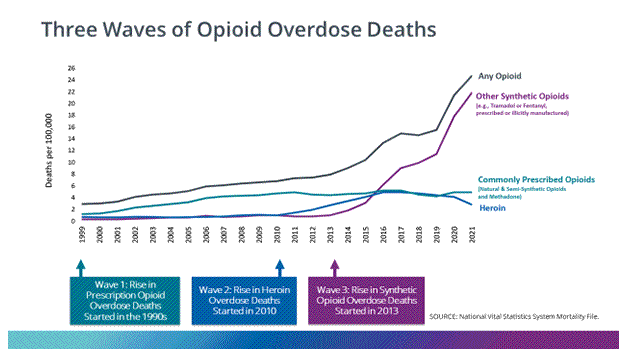 Millions of people in the U.S. are living with opioid use disorder (OUD).
Millions of people in the U.S. are living with opioid use disorder (OUD).
- Opioid use disorder (OUD) occurs when opioid use causes significant impairment and distress.
- A diagnosis of OUD is based on specific criteria such as unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control use or use resulting in a failure to fulfill obligations at work, school, or home, among other criteria.
- About 2.7 million people in the United States report suffering from OUD.
- Overdoses are a leading injury-related cause of death in the United States and appear to have accelerated during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- OUD is a medical condition that can affect anyone – regardless of race, gender, income level, or social class.
- Common treatment options for OUD include medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) (including methadone, buprenorphine, naltrexone).
Medication opioid use disorder
The College of Family Physicians of Canada reports "Incidence of OUD associated with prescribed opioids in chronic pain patients is likely about 3% (over 2 years) but causation is uncertain. Patients with no history of substance use disorder (SUD) appear to be at lower risk (< 1%). Factors associated with increased risk include history of SUD and receiving opioids for longer (> 90 days) or at higher doses (> 120 mg/d morphine equivalent [ME])" (Moe. 2019).
 The 2022 CDC Guideline for prescribing opioids for Pain states "Before starting and periodically during continuation of opioid therapy, clinicians should evaluate risk for opioid- related harms and discuss risk with patients. Clinicians should work with patients to incorporate into the management plan strategies to mitigate risk, including offering naloxone".
The 2022 CDC Guideline for prescribing opioids for Pain states "Before starting and periodically during continuation of opioid therapy, clinicians should evaluate risk for opioid- related harms and discuss risk with patients. Clinicians should work with patients to incorporate into the management plan strategies to mitigate risk, including offering naloxone".
To encourage people to assist an individual who is, or may be suffering an overdose, many states have also enacted laws which protect laypeople who administer naloxone, in good faith, in an emergency from civil and/or criminal liability. As of July 2022, all 50 states and the District of Columbia have some form of a naloxone access law (LEGISLATIVE ANALYSIS AND PUBLIC POLICY ASSOCIATION 2022).
Addiction refers to psychological dependence on a specific drug and is characterized by a pattern of compulsive drug use, including continued craving for the opioid drug and the need to use the drug for effects other than pain relief. The associated behaviors include impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving for the drug.
Tolerance and physical dependence occur in many patients after one to four weeks of regular use of opioid drugs. Under appropriate medical supervision, opioid use alone is not the major factor in the development of addiction. Other biochemical, social, and psychological factors also play an important role in the development of addiction; addiction is a disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors that influence its development and manifestations.
It is vital that nurses are educated about the current research on opioids and addiction. The percentage of the population with chronic pain is increasing. In addition, the population is aging and patients with malignant pain due to cancer are living longer.
Instant Feedback:
Patients who exhibit tolerance to an opioid analgesic are likely to become addicted.
References
Legislative Analysis and Public Policy Association | Health Data. (2022). https://legislativeanalysis.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Naloxone-Access-Summary-of-State-Laws.pdf
Moe, S., Kirkwood, J., & Allan, G. M. (2019). Incidence of iatrogenic opioid use disorder. Canadian family physician Medecin de famille canadien, 65(10), 724.
Theriot J, Sabir S, Azadfard M. Opioid Antagonists. [Updated 2023 Jul 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537079/
 Opioid use disorder and opioid addiction remain at epidemic levels in the U.S. and worldwide. Three million US citizens and 16 million individuals worldwide have had or currently suffer from opioid use disorder (OUD).(Azadfard et al., 2023). The increase in OUD can be partially attributed to overprescribing of opioid medications. Healthcare providers in the 1990s increased opioid prescribing in response to the "pain as fifth vital sign" campaign.
Opioid use disorder and opioid addiction remain at epidemic levels in the U.S. and worldwide. Three million US citizens and 16 million individuals worldwide have had or currently suffer from opioid use disorder (OUD).(Azadfard et al., 2023). The increase in OUD can be partially attributed to overprescribing of opioid medications. Healthcare providers in the 1990s increased opioid prescribing in response to the "pain as fifth vital sign" campaign.
