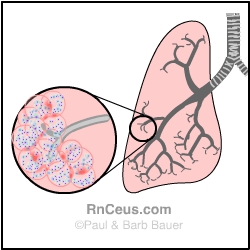

Pneumonia: An infection in lung tissues causes the alveoli to become swollen and porous (as in the above diagram), so red and white blood cells move from the bloodstream into the alveoli. The alveoli become consolidated (filled), with bacteria, fluid and blood cells, any of which can reduce ventilation and gas exchange.
| Assessment findings include: | |
|
Inspection |
Symptoms of infection: fever, sweating, chills Signs of Pneumonia
|
|
Palpation |
|
|
Percussion |
|
|
Auscultation |
|
Instant Feedback:
©RnCeus.com