Medical Treatment
The goal of hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment has evolved. Just a few years ago the goal was to slow the progression of the disease. Today the goal is to obtain a sustained virological response (SVR) i.e. undetectable HCV RNA 12-24 months after treatment. SVR is considered a cure and has been associated with decreases in all-cause mortality, liver-related death, the need for liver transplantation, hepatocellular carcinoma rates, and liver-related complications.
Recent pharmaceutical advances have produced fully oral, direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment regimens that yield nearly 100% SVR for most patient populations. Current guidelines strongly recommend treatment "for all patients with chronic HCV infection, except those with a short life expectancy that cannot be remediated by HCV therapy, liver transplantation, or another directed therapy. Patients with a short life expectancy owing to liver disease should be managed in consultation with an expert (AASLD 2017)."
There is a recommended, interferon and ribavirin free, oral dosed, combination DAA regimen for nearly all patients. DAA therapy is short duration (8-12 weeks), well tolerated and powerfully effective treatment but it must be patient-specific to achieve an optimum outcome.
Some factors that influence the selection of an appropriate drug regimen may include:
-
HCV genotype
- Types GT1a, GT1b, GT2, GT3, GT4, GT5, GT6,
- The presence of baseline NS5A resistant substitutions (RASs)
- cirrhosis or fibrosis
- renal impairment
- previous HCV treatment
- co-infections
- post-transplant
FDA approved DAAs are designed to act at critical points in the HCV lifecycle. After entering the host cell viral RNA is translated to produce one long inactive polyprotein chain of ten viral proteins. Both host and viral proteases are necessary to cleave the long chain into ten functional viral proteins. The virus cannot replicate if the long chain polyprotein is not cleaved or the proteins are not free to carry out their respective functions.
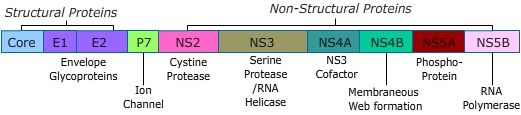
There are three classes of approved DAAs.
- NS3/4A protease inhibitors - boceprevir, glecaprevir, grazoprevir, simeprevir, Paritaprevir, Telaprevir, Voxilaprevir
- NS5A inhibitors - daclatasvir, elbasvir, ledipasvir, ombitasvir, pibrentasvir, velpatasvir
- NS5B polymerase inhibitors - sofosbuvir, dasabuvir
Recommended drug combinations |
|
Recommended Regimen |
Approved genotypes |
| Grazoprevir/elbasvir | 1, 4 |
| Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir | 1, 4, 5, 6 |
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir | 1,2,3,4,5,6 |
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir | 1,2,3,4,5,6 |
| Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir | 1,2,3,4,5,6 |
Reference
AASLD-IDSA. Recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C. http://www.hcvguidelines.org. Accessed 2/15/18