Risk
Factors
Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) of all races and ethnicities remain the population most severely affected by HIV. CDC estimates that MSM account for just 2% of the US population, but accounted for 61% of all new HIV infections in 2009. MSM accounted for 49% of people living with HIV infection in 2008 (the most recent year prevalence data are available).
Socioeconomic factors have been shown to influence the incidence of sexually transmitted disease (STD). Age, gender, sexuality, education, poverty, race, unequal access to quality healthcare and prevalence of infection within a community all can affect the risk of contracting an STD.
Black and hispanic Americans are disproportionately affected by HIV. Blacks represent approximately 14% of the US population, but accounted for an estimated 44% of new HIV infections in 2009. Latinos represented 16% of the population but accounted for 20% of new HIV infections in 2009. In the same year, the estimated rate of new HIV infections among black women was 15 times that of white women and over three times that of
Latina women.
Instant
Feedback:
Race
is a risk factor for HIV infection.
Risk factors are
related to the following:
 Poverty/socioeconomic
factors:
Poverty/socioeconomic
factors:
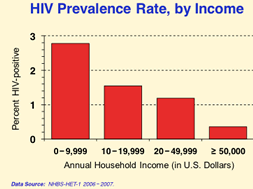
"Poverty is the single most important demographic factor associated with HIV infection among inner-city heterosexuals."* Demming and DiNenno found that the HIV prevalence rates in urban poverty areas are inversely related to annual household income; the lower the income,the greater the HIV prevalence rate. They also found that "the inverse relationship between HIV prevalence and socioeconomic status (SES) was observed for all SES metrics examined (education, annual household income, poverty level, employment, and homeless status)."
Youth:
Young
people continue to be at risk for HIV infection and are becoming HIV infected
in increasing numbers. This risk is more pronounced for minority and ethnic
youth in the US. According to CDC’s Youth Risk Behavioral Survey (YRBS), many young people begin having sexual intercourse at early ages: 47% of high school students have had sexual intercourse, and 7.4% of them reported first sexual intercourse before age 13. HIV/AIDS education needs to take place at correspondingly young ages, before young people engage in sexual behaviors that put them at risk for HIV infection.*
Heterosexual transmission:
Heterosexual contact poses a significant risk for women. Females are at increased risk due to amplified socioeconomic disparities combined with physiologic factors: *
- The adolescent cervix contains more single-layer columnar cells which provide less barrier protection.
- Asymptomatic sexually transmitted infections are more prevalent in females and theses infections may enhance transmission of HIV infection.
- Female reproductive anatomy provides greater susceptible surface area (cervical epithelium and the mucosa of the vagina) is many times greater than that of the male (urethra, glans and foreskin).
- The cervical os can allow viral passage to the upper reproductive tract.
Male circumcision has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of HIV acquisition by men during penile-vaginal sex.
- the foreskin is more susceptible to epithelial disruption during sex, then the rest of the penis.
- higher rates of STD genital ulcers are observed in men with uncircumcised penis.
- the inner mucosal surface of the foreskin has a high density of CD4+ (langerhans) cells.
Men having sex with other
men (MSM):
MSM represents about 2% of the population but accounted for about 61% of new HIV infections among U.S. males in 2009. Risky behaviors are higher among young MSM than among older MSM. *
Sexually transmitted
diseases:
Individuals
who are infected with STDs are three to five times more likely than non-infected
individuals to acquire HIV, if exposed to the virus through sexual contact.
In addition, if an HIV-infected individual is also infected with another STD,
that person is 3 to 5 times more likely than other HIV-infected persons, to
transmit HIV through sexual contact. In the United States, over 12 million people
develop STDs each year, and most of these people are under age 25.
Homelessness/runaways:
Young people who are homeless or runaways, often engage in substance
abuse, which can increase the risk for HIV infection. They may exchange
sex for drugs or money, believing this is their only chance of survival on
the
streets.
Homelessness
is not just a problem of young people. Studies indicate that between 3-20%
of homeless people are infected with HIV, with some subgroups having much
higher
rates. Also, surveys have indicated that homeless rates for those with HIV/AIDS
are increasing. Because people with HIV/AIDS often lose their jobs or are
unable
to work, many will become homeless at some point.
Substance abuse:
Young
people (18-24) who use alcohol, tobacco, or other drugs are more likely to engage
in high-risk behaviors, such as unprotected sex, when they are under the influence
of drugs or alcohol. Substance abuse is also a risk factor for other age groups. People infected through injection drug use accounted for 19% of all people living with HIV . Sixteen percent of men and 26% of women living with HIV were infected through injection drug use.
Medical procedures/Needlestick
injuries:
Medical practices associated with HIV transmission include:
- exposure to contaminated devices and equipment
- transfusion of HIV contaminated
blood,
- transplantation of HIV contaminated
tissue and organs,
- needlestick injuries
- exposure of mucous membranes,
and even supposed "intact" skin to HIV-contaminated blood and body fluid.
Needlestick injuries are
a major concern for people in the
healthcare industry. While the
risk for HIV transmission from needlestick is low, it is still a significant
danger. A study
of syringes used to administer medications to people with HIV showed 3.8%
had detectable HIV RNA. Moreover, in a study of the viability of the virus
in needles, viable HIV was found in 8% at 21 days, when the needles had
been
stored
at room temperature.
HIV positive children
becoming adults:
Many children who were infected through perinatal transmission
are now becoming young adults, and making decisions about sexual behavior.
Perinatal Transmission:
The number of new perinatal infections each year has steadily declined
since 1994. At that time, a zidovudine regimen given prenatally, intrapartum,
and to the newborn, was shown to reduce the risk of mother-to-child transmission
by two thirds. However, the CDC estimates that between 280-370 neonates continue
to be
infected every year. Of those infected, 40% were born to mothers whose HIV
status at delivery was unknown. CDC recommends universal HIV testing of pregnant
women and routine rapid HIV testing using the
opt-out approach for all women in labor whose HIV status is unknown.
Instant
Feedback:
Women
in labor,
whose HIV status is unknown, may opt-out of HIV testing.
Severe
mental illness:
Adults
with severe mental illness have been disproportionately affected by the HIV/AIDS
epidemic. Studies have shown that the majority of adults with severe mental
disorders are sexually active and many engage in high-risk behaviors, such as
unprotected sex, multiple sexual partners, and IV drug use.
Older adults engaging
in unsafe sex:
With improvement in health care, and the availability
of drugs like Viagra, many older adults are remaining sexually active.
Some older
males have contact with prostitutes, as well as multiple sexual partners. About
10% of those with AIDS are over age 55 and 1 in 25 cases of AIDS in the
U.S.
are people 65 years old and older.
Estimated per-act
risk for acquisition of HIV •
Exposure
route |
Risk per 10,000 Exposures |
Transfusion 1 unit infected blood |
9,000 |
Needle-sharing during injection drug use |
67 |
Percutaneous (needle-stick) |
30 |
Receptive anal intercourse |
50 |
Receptive penile-vaginal intercourse |
10 |
| Insertive anal intercourse |
6.5 |
| Insertive penile-vaginal intercourse |
5 |
| Receptive oral intercourse |
low |
| Insertive oral intercourse |
low |
| Biting |
negligible |
| Spitting |
negligible |
| Throwing body fluids (including semen or saliva) |
negligible |
| Sharing sex toys |
negligible |
Instant
Feedback:
The
highest estimated per-act risk for acquisition of HIV involves needle
sharing for drug use.
 Poverty/socioeconomic
factors:
Poverty/socioeconomic
factors: