Nursing Boards and Organizations
State Boards of Nursing (BON) are committees established by law to regulate the practice of nursing. The purpose of the BON is to protect the public's health by ensuring safe nursing practices within its jurisdiction.
State California
California Code of Regulations - Title 16, Article 7. 1470
The Board of Registered Nursing in conjunction with the Medical Board of California intends, by adopting the regulations contained in the article, to jointly promulgate guidelines for the development of standardized procedures to be used in organized health care systems which are subject to this rule. The purpose of these guidelines is:
(a) To protect consumers by providing evidence that the nurse meets all requirements to practice safely.
(b) To provide uniformity in development of standardized procedures.Florida Florida TITLE XXXII
Chapter 464.002 Purpose.—The sole legislative purpose in enacting this part is to ensure that every nurse practicing in this state meets minimum requirements for safe practice. It is the legislative intent that nurses who fall below minimum competency or who otherwise present a danger to the public shall be prohibited from practicing in this state.
464.006 Rulemaking authority.—The board has authority to adopt rules pursuant to ss. 120.536(1) and 120.54 to implement the provisions of this part conferring duties upon it.Louisiana TITLE 46 - Chapter 31
The Louisiana State Board of Nursing is a legally created administrative agency acting within the governmental structure of the state and possessing legal power. To safeguard life and health of the citizens of Louisiana, the law governing the practice of registered nursing, as re-enacted and amended, delegates to this board the responsibility to establish and publish standards of nursing practice; to regulate the practice of nursing by the registered nurse and the advanced practice registered nurse; to provide for examination and licensure of the nurse practicing as a registered nurse and an advanced practice registered nurse; and to establish standards for educational programs preparing individuals for nursing practice.Texas
TITLE 22, PART 11, CHAPTER 211, Rule §211.2 "The purpose of the board is to protect and promote the welfare of the people of Texas. This purpose supersedes the interest of any individual, the nursing profession, or any special interest group."
Each state legislature determines the composition and organization of its BON. Membership may include RNs, LPNs, ARNPs, consumer advocates, etc. In some states the BON is also responsible for regulation of nursing assistant programs.•
State BONs usually have the following responsibilities and powers:
Instant Feedback:
The duty of your BON is to protect the public by ensuring the safe practice of nursing.
It is within the purview of the state board of nursing to discipline individuals for violations of the NPA. It is also within their purview to ensure the right of the nurse to perform all of the lawful activities described in the nursing practice act.• It is not lawful for any entity, e.g., physician, organization or institution, to abridge or expand the boundaries of nursing practice without approval from the BON.
Disciplinary action
The sections Chapter 456, 454, and 64B9 contain specific regulations. Nurses reported for conduct that violates these regulations are so charged.
STIPULATED LAW
- Respondent admits that he/she is subject to the provisions of Chapters 456 and 464, Florida Statutes, and the jurisdiction of the Department and the Board.
- Respondent admits that the stipulated facts, if proven true, constitute violation of Chapter 465 and/or 464, Florida Statutes as alleged in the Administrative Complaint.
When a nurse is charged with breaking these laws, their name is a public record that includes a description of the offense and how it is adjudicated. Some of the recent crimes brought before the Florida and other State Boards of Nursing include withholding pain medication to patients, using another nurse's license number, leaving medications at the bedside, committing Medicare fraud, practicing with a delinquent license, and other offenses. Read the laws carefully!
State boards of nursing also regulate continued competency requirements for licensure renewal. To date 38 states plus DC, require some type of continuing education for RNs and LPNs usually during a two-year period. The number of contact hours and the type of requirements vary from state to state. The number of contact hours range from 15 to 30 every two years. Usually these are obtained through continuing education courses offered by approved providers. Some states waive contact hours requirements if the nurse is engaged in nursing practice. Some states give credit for nursing presentations, published nursing articles, and research studies.
Some states have specific requirements for the type of courses that must be taken. For example, nurses licensed in Florida are required to complete 24 contact hours every two years encompassing the following topics:
Instant Feedback:
All states require nurses to acquire 30 contact hours of continuing education every two years.
Nursing organizations
The American Society of Superintendents of Training Schools of Nursing formed our first nursing organization in 1893. Today this organization exists as the National League for Nurses (NLN). The NLN continues to advocate for excellence in nursing education through its goal to be "the primary source of data for legislation, regulations, or decisions about nursing education and the nurse educator workforce".•Licensing of nurses was the goal of our second nurse organization, the Nurses' Associated Alumnae of the United States and Canada. They were founded in 1896 and are known today as the American Nurses Association (ANA). The ANA is America's largest and most influential nursing organization. It seeks to advance the nursing profession by "fostering high standards of nursing practice, promoting the rights of nurses in the workplace, projecting a positive and realistic view of nursing, and by lobbying the Congress and regulatory agencies on health care issues affecting nurses and the public." The ANA represents nurses at the state level through its Constituent and State Nursing Associations.
In 1978, the American Nurses Association (ANA) Council on State Boards of Nursing recognized that their mission would be better served by forming a national independent organization focused on providing regulatory excellence for public health, safety and welfare. The National Council on State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) was formed. "NCSBN is devoted to developing a psychometrically sound and legally defensible nurse licensure examination consistent with current nursing practice. NCSBN became the first organization to implement computerized adaptive testing (CAT) for nationwide licensure exams in 1994. In addition to the NCLEX-RN and NCLEX-PN examinations, NCSBN also develops and administers the largest competency evaluation for nurse aides known as the National Nurse Aide Assessment Program (NNAAP)."• Finally, the NCSBN manages the Nursys database which contains national information on nurse licensure that is publically available. If a nurse applies for a license in a different state, if their former state is connected with the Nursys database, the nurse’s license activity can be obtained quickly.
Instant Feedback

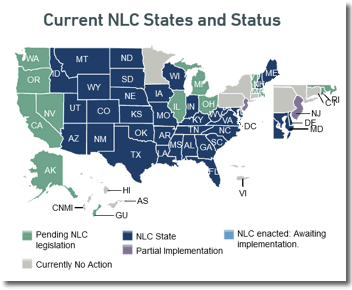
The 34 NLC Member States |
||||||
| • Alabama | • Florida | • Kansas | • Mississippi | • New Jersey | • South Carolina | • Virginia |
| • Arizona | • Georgia | • Kentucky | • Missouri | • New Mexico | • South Dakota | • West Virginia |
| • Arkansas | • Idaho | • Louisiana | • Montana | • North Carolina | • Tennessee | • Wisconsin |
| • Colorado | • Indiana | • Maine | • Nebraska | • North Dakota | • Texas | • Wyoming |
| • Delaware | • Iowa | • Maryland | • New Hampshire | • Oklahoma | • Utah | |
© RnCeus.com